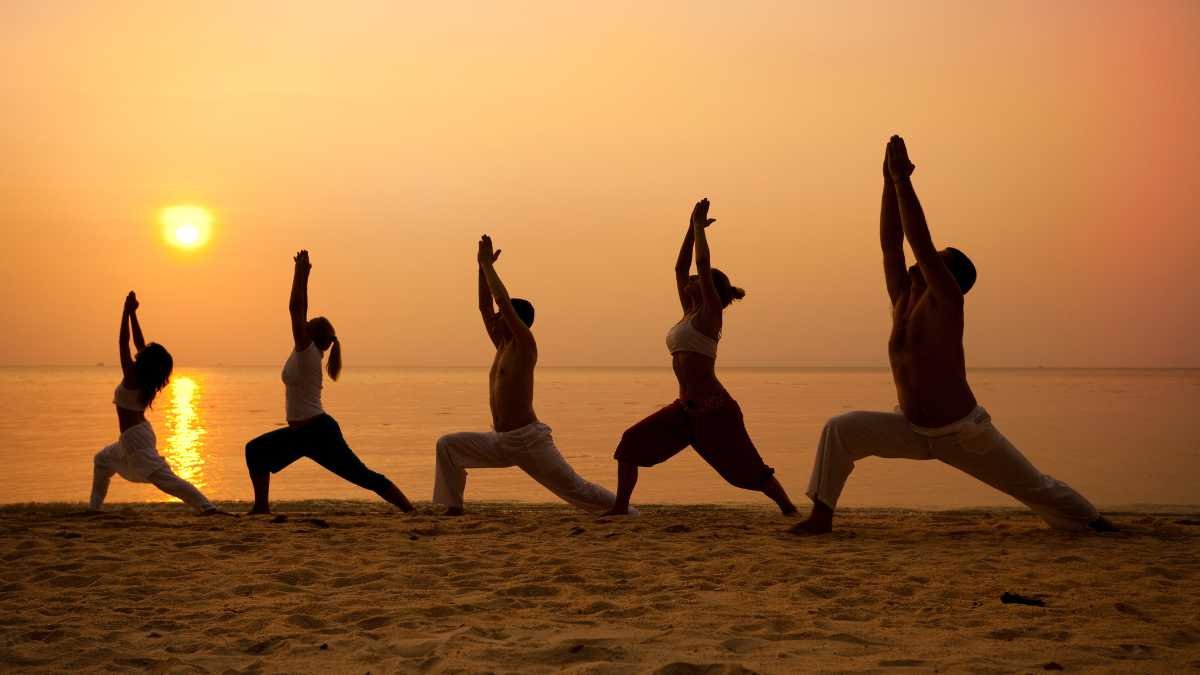
Yoga, an ancient practice rooted in India, has achieved worldwide prominence owing to its holistic benefits. Combining physical postures, breath control, meditation, and ethical principles, yoga enhances physical fitness, mental clarity, stress reduction, and spiritual growth. It gained traction in the West through influential figures and its resonance with modern lifestyles, offering solace amid hectic routines.
Yoga’s significance transcends borders and cultures, fostering unity in its pursuit of well-being. Its principles of mindfulness, compassion, and self-awareness promote mental peace and emotional equilibrium. International Yoga Day and global events showcase its impact.
Ancient Origins of Yoga
The ancient origins of yoga can be traced back thousands of years to the Indus Valley Civilization, which thrived in the region that is now modern-day India and Pakistan from approximately 3300 to 1300 BCE. While the exact details are shrouded in the mists of time, archaeological evidence suggests that the roots of yoga began to take shape during this ancient civilization.
Yoga’s evolution continued through the Vedic period (around 1500 to 500 BCE), during which sacred texts called the Vedas were composed. These texts contain hymns, rituals, and philosophical teachings that laid the groundwork for yogic thought. The Upanishads, a later body of texts, delved deeper into spiritual concepts and meditation practices, further shaping the path of yoga.
It was in the subsequent centuries that renowned texts like the “Yoga Sutras” of Patanjali consolidated various yogic practices into a systematic framework. This foundational text outlined the Eight Limbs of Yoga, providing a comprehensive guide to ethical, physical, mental, and spiritual growth.
Philosophical Foundation of Yoga:
The philosophical foundations of yoga are rooted in ancient Indian thought and encompass a profound understanding of human existence, consciousness, and the nature of reality. Central to these foundations are several key philosophical systems that have shaped the principles and practices of yoga.
1. Vedanta: Vedanta philosophy explores the nature of reality and the relationship between the individual soul (Atman) and the ultimate reality (Brahman). This school of thought emphasizes self-realization and the unity of all beings.
2. Samkhya: Samkhya philosophy provides a conceptual framework for understanding the universe through the analysis of twenty-five fundamental principles (tattvas). It examines the duality between the physical world and the eternal self (Purusha).
3. Yoga: The philosophy of yoga, as outlined in Patanjali’s “Yoga Sutras,” focuses on the control of the mind and senses. It presents the Eight Limbs of Yoga, which include ethical principles (yamas and niyamas), postures (asanas), breath control (pranayama), and meditation, aiming for self-realization and liberation (moksha).
4. Bhakti: Bhakti philosophy emphasizes devotion and love for a higher power, cultivating a sense of surrender and humility. It sees the path of love and devotion as a means to unite with the divine.
5. Karma: Karma philosophy revolves around the law of cause and effect. It highlights the importance of right action, selfless service, and the notion that our actions shape our present and future experiences.
These philosophical systems provide the theoretical underpinning for yogic practices, guiding individuals toward self-realization, inner peace, and a deeper understanding of existence.
Classical Period of Yoga
The Classical Period of Yoga refers to a historical phase during which the principles, practices, and philosophies of yoga were systematically organized and refined. This era is marked by the codification of yogic ideas into comprehensive frameworks that laid the foundation for various yoga traditions as we know them today.
One of the key texts that emerged during the Classical Period is Patanjali’s “Yoga Sutras.” Compiled around 200-400 CE, this seminal work outlines the Eight Limbs of Yoga, providing a systematic guide to ethical behavior, physical postures, breath control, sense withdrawal, concentration, meditation, and ultimate liberation. Patanjali’s Yoga Sutras remain a central reference for understanding the path of yoga and its multifaceted nature.
During this period, several other classical texts also contributed to the development of yogic thought. The Bhagavad Gita, a part of the Indian epic Mahabharata, explores different paths of yoga, emphasizing devotion (bhakti), selfless action (karma), and knowledge (jnana).
Hatha Yoga, which focuses on physical postures (asanas), breath control (pranayama), and energy channeling (nadis), began to gain prominence during this era. Texts like the “Hatha Yoga Pradipika” and the “Gheranda Samhita” were composed, detailing practices for physical purification and spiritual evolution.
The Classical Period of Yoga represents a consolidation of earlier philosophical ideas and practices into more structured systems. It laid the groundwork for various yoga schools and traditions that would evolve over the centuries, while also emphasizing the ultimate goal of yoga: self-realization and liberation (moksha). This period’s contributions continue to influence modern yoga practices and philosophies, showcasing the enduring relevance of these ancient teachings.
Evolution and Adaptation
The evolution and adaptation of yoga over the centuries have been characterized by the assimilation of diverse philosophical, cultural, and geographical influences, resulting in a rich tapestry of practices and traditions.
Historical Evolution
Yoga’s evolution can be traced from its ancient roots in the Indus Valley and Vedic periods to its systematic codification in texts like Patanjali’s “Yoga Sutras.” During the Medieval Period, various schools of yoga emerged, each emphasizing distinct paths to spiritual realization. Hatha Yoga gained prominence with its focus on physical postures and breath control. Bhakti, Jnana, Karma, and Raja Yoga developed as paths to self-realization.
Diverse Traditions
Today, yoga encompasses a wide range of traditions and styles, from traditional Hatha and Raja Yoga to more contemporary forms like Vinyasa, Ashtanga, and Bikram Yoga. Each tradition caters to different needs and preferences, making yoga adaptable to diverse lifestyles.
yoga’s evolution and adaptation reflect its timeless and universal appeal. As it continues to embrace new ideas and contexts, yoga remains a versatile and inclusive practice that enriches lives across the globe. Its ability to bridge ancient wisdom with modern needs highlights its enduring significance.
Yoga in Modern India and Its Global Impact on Well-Being
Yoga, an ancient practice rooted in Indian traditions, has evolved significantly over the years to become a global phenomenon. While its origins trace back thousands of years, yoga in modern India continues to flourish, adapting to contemporary lifestyles while preserving its rich heritage. As more people worldwide recognize the benefits of yoga, it has become an essential tool for holistic well-being, offering physical, mental, and spiritual enrichment.
The Evolution of Yoga in Modern India
In India, yoga has undergone significant transformations, from being a spiritual practice to a mainstream wellness discipline. Institutions dedicated to yoga teacher training in India have played a crucial role in popularizing it by offering structured programs that blend traditional wisdom with modern scientific research. With the increasing recognition of yoga’s benefits, many educational institutions and health centers now incorporate it into their curricula and wellness programs.
The Indian government has also actively promoted yoga through initiatives such as International Yoga Day and the establishment of specialized yoga universities. Additionally, growing interest in yoga teacher training courses in India has led to an expansion of certified programs, making it easier for individuals to become professional instructors and spread the benefits of yoga worldwide.
The Importance of Yoga in Global Well-Being
Yoga is no longer confined to India; its influence extends across the world, helping people achieve better physical and mental health. The holistic nature of yoga allows practitioners to develop flexibility, strength, and mindfulness. Many individuals seeking an authentic experience opt for India yoga teacher training, where they gain in-depth knowledge and hands-on practice under experienced instructors.
A major reason for yoga’s increasing global appeal is its accessibility. Whether practiced in a traditional setting or through online platforms, yoga offers a means of self-care that aligns with modern lifestyles. This widespread acceptance has also led to a rise in specialized training programs, with students traveling to India to learn to teach yoga in India and immerse themselves in its cultural roots.
Yoga Retreats and Their Role in Well-Being
For those seeking relaxation and rejuvenation, yoga retreats provide an ideal escape. A yoga retreat in Goa, for instance, offers participants an opportunity to engage in daily yoga sessions, meditation, and mindfulness exercises amidst a tranquil coastal setting. These retreats not only enhance physical well-being but also foster emotional balance and spiritual growth.
The popularity of Goa yoga retreats reflects the increasing demand for wellness tourism, where individuals prioritize self-care and holistic health experiences. Retreats serve as immersive environments for deepening one’s yoga practice while benefiting from nature’s healing effects. Many attendees also use these experiences as a stepping stone to enroll in a yoga TTC in India, furthering their journey as practitioners or instructors.
The Scientific Backing of Yoga’s Benefits
Modern scientific studies continue to validate the health benefits of yoga. Research has shown that regular practice can reduce stress, improve cardiovascular health, and enhance cognitive function. The integration of yoga into medical and therapeutic practices further supports its significance in global health.
Medical professionals and wellness experts increasingly recommend yoga as a complementary therapy for chronic conditions such as anxiety, depression, and hypertension. This growing recognition has encouraged individuals worldwide to seek authentic yoga training in India, where they can study the practice in depth and integrate it into their personal and professional lives.
Bridging Traditional Wisdom and Modern Needs
The adaptability of yoga allows it to cater to diverse needs. While some focus on the spiritual aspects, others prioritize its physical benefits. Yoga teacher training courses in India cater to both perspectives by combining classical teachings with modern applications. As a result, yoga teachers worldwide are equipped to offer classes that appeal to different demographics, from fitness enthusiasts to those seeking mental peace.
Many international practitioners choose to undergo yoga teacher training India programs because they provide a structured yet immersive experience. With a strong foundation in philosophy, anatomy, and teaching methodologies, these programs help individuals refine their practice and gain the expertise needed to guide others.
The Future of Yoga and Its Global Impact
As the world faces increasing health challenges, yoga stands as a beacon of holistic wellness. The rise in lifestyle-related disorders and mental health issues highlights the need for sustainable well-being practices, making yoga more relevant than ever. India yoga teacher training programs continue to attract individuals from different backgrounds, fostering a global community of practitioners dedicated to spreading wellness through yoga.
Additionally, technological advancements have made yoga more accessible than ever. Online platforms offer courses, live sessions, and virtual retreats, allowing people worldwide to benefit from yoga without geographical limitations. Nevertheless, many still prefer in-person training, traveling to India for yoga teacher training courses in India to gain firsthand experience from traditional practitioners.
Impact on Health and Well-being
The practice of yoga in modern India has had a significant impact on health and well-being, addressing physical, mental, and emotional aspects. Here’s how:
- Physical Fitness: Yoga’s emphasis on asanas (postures) promotes flexibility, strength, and balance. Regular practice can improve muscular tone, joint health, and overall physical conditioning.
- Stress Reduction: Yoga incorporates relaxation techniques, deep breathing, and meditation, which help reduce stress, anxiety, and promote mental clarity.
- Mental Health: The mind-body connection in yoga enhances mental well-being. Mindfulness and meditation practices can alleviate symptoms of depression, enhance emotional resilience, and improve overall mental health.
- Flexibility and Mobility: Yoga’s focus on stretching and elongating muscles increases joint range of motion, preventing injuries and improving mobility, particularly beneficial as people age.
- Pain Management: Yoga can alleviate chronic pain conditions such as lower back pain, arthritis, and migraines through gentle movement, relaxation, and improved body awareness.
Principle and prerequisite for Aasan
- One can practice asana 3-4 hrs after- solid food, 1 hrs after- liquid or juices and ½ hr after- water.
- Advanced asana should always be performed with a clear bowel.
- Avoid any kind of jerky movement or outside pressure which may lead to injury.
- During asana, wearing loose and comfortable clothes is very much necessary for energy flow.
- In acute disease or any abnormal pain avoid asana.
- Females should not practice any advanced asana during the 3 days menstrual period.
- During pregnancy any asana which increase abdominal pressure must be avoided
- Before taking particular pursuit of asana one should be clear with objective.
- Asana should be performed in very slow and rhythmic manner
Conclusion
Yoga’s journey spans millennia, originating in ancient India as a spiritual and meditative practice. Rooted in Hindu and later Buddhist traditions, yoga evolved through various schools of thought, emphasizing self-realization and transcending the limitations of the physical world. Over centuries, yoga’s teachings were passed down orally and through texts like the Yoga Sutras.In the late 19th and 20th centuries, yoga gained attention globally, facilitated by Indian gurus who introduced it to the West. It transformed from a niche practice into a diverse, widely embraced phenomenon, emphasizing physical fitness, stress reduction, and holistic well-being. Today, yoga is a global cultural and wellness phenomenon, celebrated for its ancient wisdom adapted to modern lifestyles.
Yoga in modern India remains deeply rooted in its traditional essence while evolving to meet contemporary needs. It plays a vital role in global well-being by offering a holistic approach to health, balancing physical fitness, mental clarity, and spiritual awareness. From engaging in a Goa yoga retreat to enrolling in a yoga TTC in India, individuals worldwide continue to embrace yoga as a transformative practice. As its influence grows, yoga is poised to remain a fundamental aspect of holistic health and well-being for generations to come.